Medical CityAsia’s leading medical research base, Kobe Biomedical Innovation Cluster
The devastation of the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake in 1995 was the catalyst to reinvent Kobe as a centre for cutting-edge life science research. Transforming a man-made island in the city harbour, it created one of the largest biomedical clusters in Japan. With universities, research institutes, hospitals, and biomedical companies all concentrated within 2 km, it is an environment that encourages collaborative research and development, and practical application. Through this collaboration, Kobe continues to generate innovative research and technologies that are changing the world.
A hotbed for the future of medicine
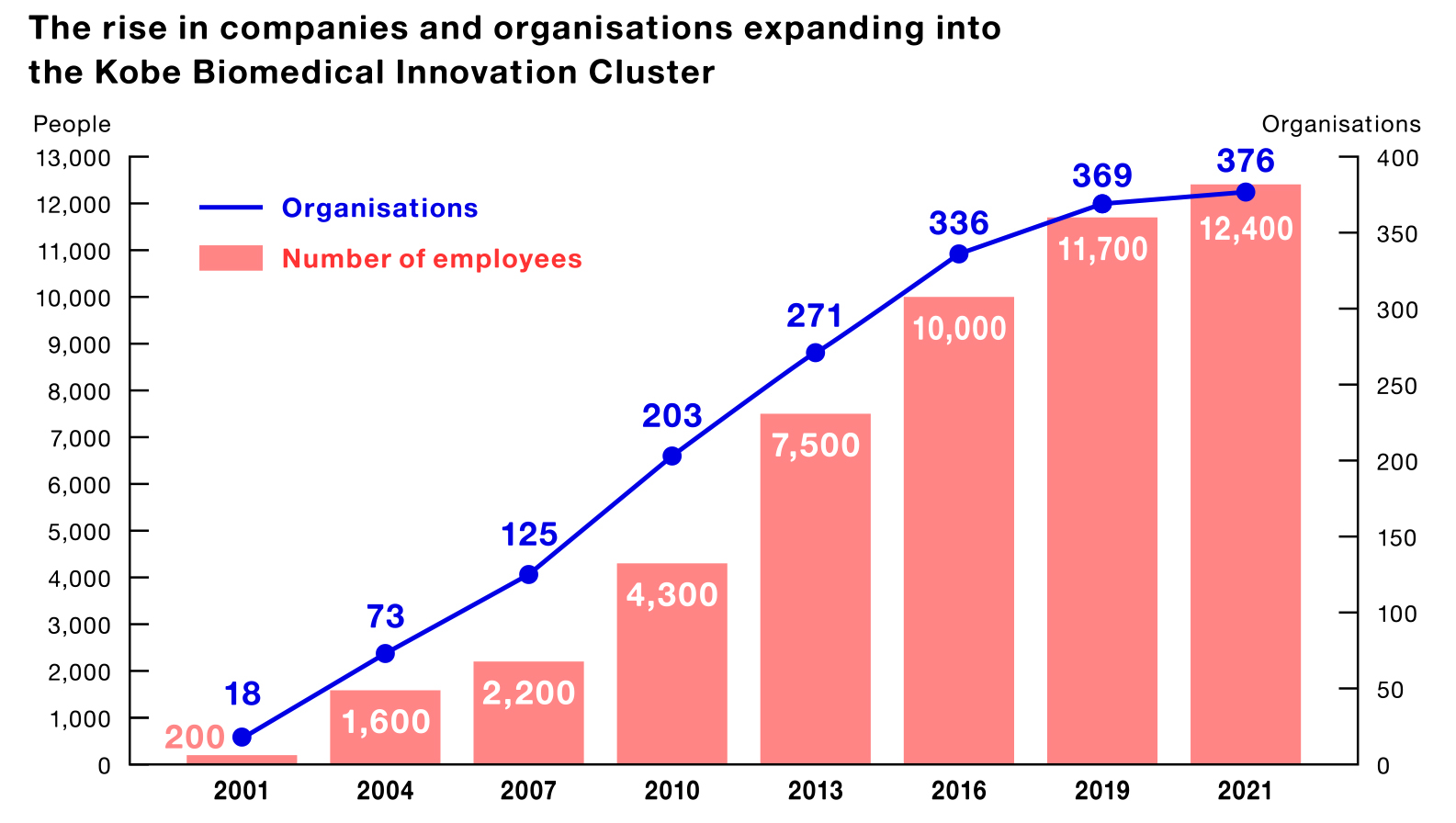
12,400 people work at approximately 370 organisations in the Kobe Biomedical Innovation Cluster. Fostering collaboration between academia, industry, and government, the cluster generates innovations and positions itself as a top biomedical cluster in Japan.
Advanced medical care x technology from Kobe
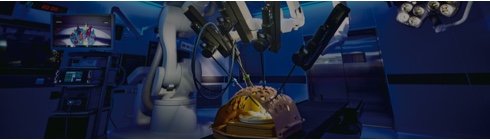
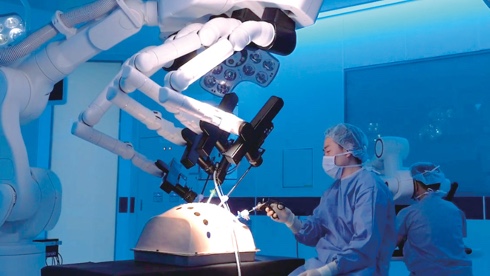
A Japan produced surgical support robot
Medicaroid Corporation* has developed the hinotori™ Surgical Robot System, in the industry-academia collaboration en-vironment of Kobe. The system was put into practical use in just 5 years, and the first surgery was successfully performed at Kobe University in December 2020.
- *A venture company funded by Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Sysmex based in Kobe.
Fugaku, A world-leading supercomputer
Fugaku, the successor to supercomputer K, began service in March 2021. Fugaku leverages the technology, human resources, and accumulated applications developed by K, to realise a versatile and internationally competitive system. Fugaku is expected to contribute to various fields, such as drug discovery and disaster prevention.
- Photo Credit:Courtesy of RIKEN

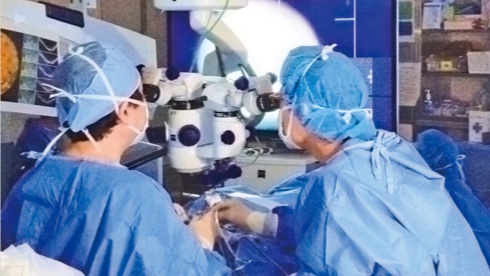
World’s first transplantation of iPS photoreceptor cells
Kobe City Eye Hospital per-formed the first transplant of iPS-developed retinal cells to treat genetic eye disease, opening up new possibilities for the use of iPS cells - which can be programmed to create any new cell - in regenerative medicine.